Application of Ultrasonic waves
SONAR is a device which stands for sound navigation and ranging.
It is based on the principle of echo sounding. In this acoustical technique highfrequency ultrasonic wave are used. When ultrasonic waves are transmitted through water, gets reflected by the object under water. The change in frequency of the echo signals due to the Doppler effect helps us to determine the velocity, distance and the direction of object.
In the absence of an obstacle the ultrasonic waves do not get reflected to the receiving transducer. But in the presence of an obstacle the ultrasonic waves get reflected and are picked up by the receiving transducer. Knowing the velocity of ultrasound and the elapsed time, the distance of the object can be determined.
Using SONAR, the distance and direction of submarines, depth of sea, depth of rocks in the sea, the shoul of fish in the sea, etc., can be determined.
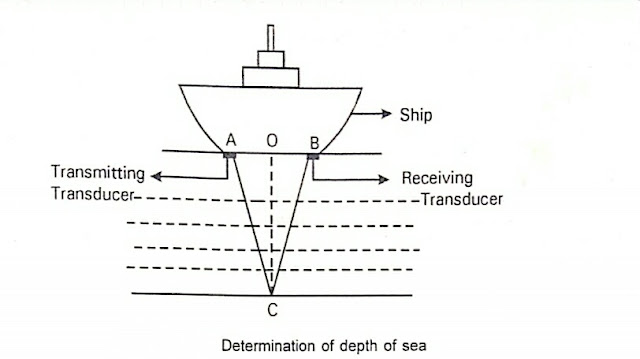
1. Determinati of Depth of Sea
The ultrasonic wave can be used to find the depth of the sea. It is based on the principle of echo sounding.
Figure illustrates the use of ultrasonic to find the depth of sea.
Figure illustrates the use of ultrasonic to find the depth of sea.
The ultrasonic waves sent from point A travel through sea water and gets reflected from the bottom of the sea. The reflected wave are received at point B.
The time taken for the ultrasonic waves to travel to the bottom of the sea and to get reflected back to the top surface is noted using a CRO. If the velocity V of the ultrasonic wave is already known, then
Thus, the depth of the sea can be calculated using this formula.
Fathometer or echometer is a device which is directly calibrated to determine the depth of the sea.
2. Cavitation
One of the major application of high power and low frequency of ultrasonic sound waves is ultrasonic processor and cleaner. In a processor and cleaner, the principal of cavitation is used.
What is cavitation?
When high frequency sound waves are passed into a solution, it produces mechanical vibration effect within the liquid. Thus the violent disturbances in the liquid results in the formation of minute vacuum bubbles (also called microscopic cavities Hor voids). This process of bubble formation and its collapse is known as cavitation.
As the sound waves continuously propagate through the liquid, each in the liquid is subjected to alternate negative and positive pressure at the complete compressions and rarefactions of the sound waves. The bubbles are grown at the microscopic level during rarefaction and it becomes very large during compression phase. As the bubbles grow larger, they become very unstable and eventually collapse in a violent implosion releasing a shock wave of energy. The resulting shock wave provide the necessary energy used to assist cleaning.
The implosion radiate high powered shockwave that dissipate repeatedly at the rate of 25000~30000 times per second. The inclusion of cavitation bubbles generate temperature of 10000°F and pressure that exceed 10000 Pa. Ultrasonic cleaning and processor used this cavitation implosion effect for cleaning.
Application
- The ultrasonic processor is used for emulsification of immiscible liquids destruction and microorganism etc.
- The ultrasonic cleaner is used to clean semiconductor components, PCBs, switches, tools, moulds, casting, gears, ball-bearing, jewelleries, coins precious stones, surgical instruments, camera lens etc.
3. Ultrasonic Cleaning
Ultrasonic cleaning system consists of an ultrasonic generator, a transducer and a tank filled with liquid cleaning solution as shown in figure.
The tank is made up of stainless steel. The ultrasonic transducer is mounted at the bottom of the tank. The size and frequency of the transducer selection depends on the capacity of the tank. The tank is filled with the cleaning liquid which may be either aqueous or solvent.
When the ultrasonic generator is switch on, it provides a suitable AC signal to the transducer and thus, the transducer generates the ultrasonic waves for desired frequency. These sound wave passed into the liquid medium within the tank and the process of cavitation occurs within the liquid. Due to cavitaion process fine particals on object are pulled into the space releasing them from the object and they become suspended in the liquid by the soup.
To increase the effect of the ultrasonic cleaning, the cleaning medium should have lower surface tension, low viscosity etc.
Advantages of ultrasonic cleaning
- Environmental pollution free and less cost.
- Enhanced cleaning speed for both solvent and aqueous medium.
- Cleaning is consequently and of high quality.H
- High safety with lesss complaintst.
- It occupies less space and reduces labour.
4. Ultrasonic Drilling and Cutting
Ultrasonics are used for making holes in very hard materials such as glass, Diamond, gems, ceramic, etc. Processing high impact brittleness.
In this drilling technique, a tool bit(drillinging device) driver by a suitable ultrasonic generator is used. Abrasives like boron carbide or silicon carbide are used. An ultrasonic produced by the generator makes the tool bit to move up and down very quickly and forces the abrasive practicles against the material to be cut thereby removing some materials from the plate. This process continuous until the desired depth of the hole is formed over the plate. The same action in ultrasonic cutting.
5. Ultrasonic welding
Ultrasonic welding is a solid state phenomenon of producing metallurgical bond between the material without melting. The ultrasonic welding is also known as a cold welding technique.
The is because, during a conventional welding process properties of some metals may get changed on heating. Therefore, they cannot be welded by electric or gas welding. In such cases, the metal sheet can be welded together at room temperature using Ultrasonic waves.
Process
The surface of the workpiece are cleaned and held together. In ultrasonic welding, bonding between two welding pieces is produced due to the local application of high frequency vibratory evenly by keeping the work piece together under pressure.
Using an ultrasonic generator, the ultrasonic vibration are transmitted into the work is through a coupling system or Sonotrode which is resting over one of the workpiece. The anvil is used to support the welding pieces and apposes the clamping force is as shown in figure.
A static clamping force is applied perpendicular to the interface between the workpieces at the same time, the sonotrode tip oscillates parallel to the interface of the workpiece. Due to the combination of static oscillating shear forces, an internal stress is created in the workpiece. As long as the internal stress is below the elastic limit, the metal deforms elastically. But, when the strees exceed the threshold value a high localised interfacial slip occurs. As a result, the breaking and discipline of the surface film take place which produces metal to metal contact at any point.
Due to friction arising between the surface, a rise in temperature of surface layer exceeds the recrystallization point. The layer melt and bond together to form a strong joint.
Application of ultrasonic welding
- It is used in variety of packaging application such as soft foil packet, pressurised cans,etc.
- It is used to weld electronic components such as
- Wires and ribbons to the thin films
- Diode and transistor to substrate
- Aluminiumm wires to semiconductor
- In a solar cell, as the connection between photovoltaic modules are made using ultrasonic welding, they are much useful in reducing the fabrication cost of solar energy ssystem.
- It is used for encapsulating the material which are sensitive to hit on electrical current.
Advantages of ultrasonic welding
- Ultrasonic welding are made without melting the material.
- It is used to join the wide variety of dissimilar metals.
- The welding time is very short and also a safe method.
6. Ultrasonic soldering
In the conventional method of soldering, prior to soldering, the surface are to be cleaned with active fulx to remove the contaminants, grease, oxide films,etc. Because, such films may prevent the formation of good joint. The fluxes when heated dissolves unwanted containment and oxide films. As a result of this, the surface readily allows the molten solder to form of a firm joint.
Using this type of conventional soldering, Aluminium foil considers, aluminimum wires and plates cannot be soldered. Hence, to solder this type of material ultrasonic welding technique (a process of soldering metal without fluxes) can be used.
An ultrasonic soldering iron consist of an ultrasonic generator having a tip fixed at its end which can be heated by an electrical heating element. The tip of the soldering iron melts to solder on the aluminium (soldering piece) and ultrasonic remove the oxide and other containments over the surface and allows to solder to fasten.




Comments
Post a Comment